Prochlorococcus Marinus Human Disease
Prochlorococcus marinus human disease. Humans are typically infected through dog and cat bites and infections can lead to swelling and arthritis around joints. Marinus SS120 the complete genome sequence reported here is an extremely low-light-adapted. Hess Humboldt-University Department of Biology Chausseestr.
Found in human microbiome Microbes that live anywhere in the human body and are not pathogenic to humans ie. This bacterium causes a range of human and animal diseases including cholera in birds hemorrhagic septicemia in cattle and atrophic rhinitis in swine. Despite its small size it.
16S rRNA has been frequently used to establish a. Immunization of mice with lipopeptide antigens encapsulated in novel liposomes prepared from the polar lipids of various Archaeobacteria elicits rapid and prolonged specific protective immunity against infection with the facultative intracellular pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. Despite its small size it.
Prochlorococcus is a photosynthetic prokaryote. 117 D-10115 BerlinGermany Correspondence WolfgangHessrzhu-berlinde. Despite its small size it.
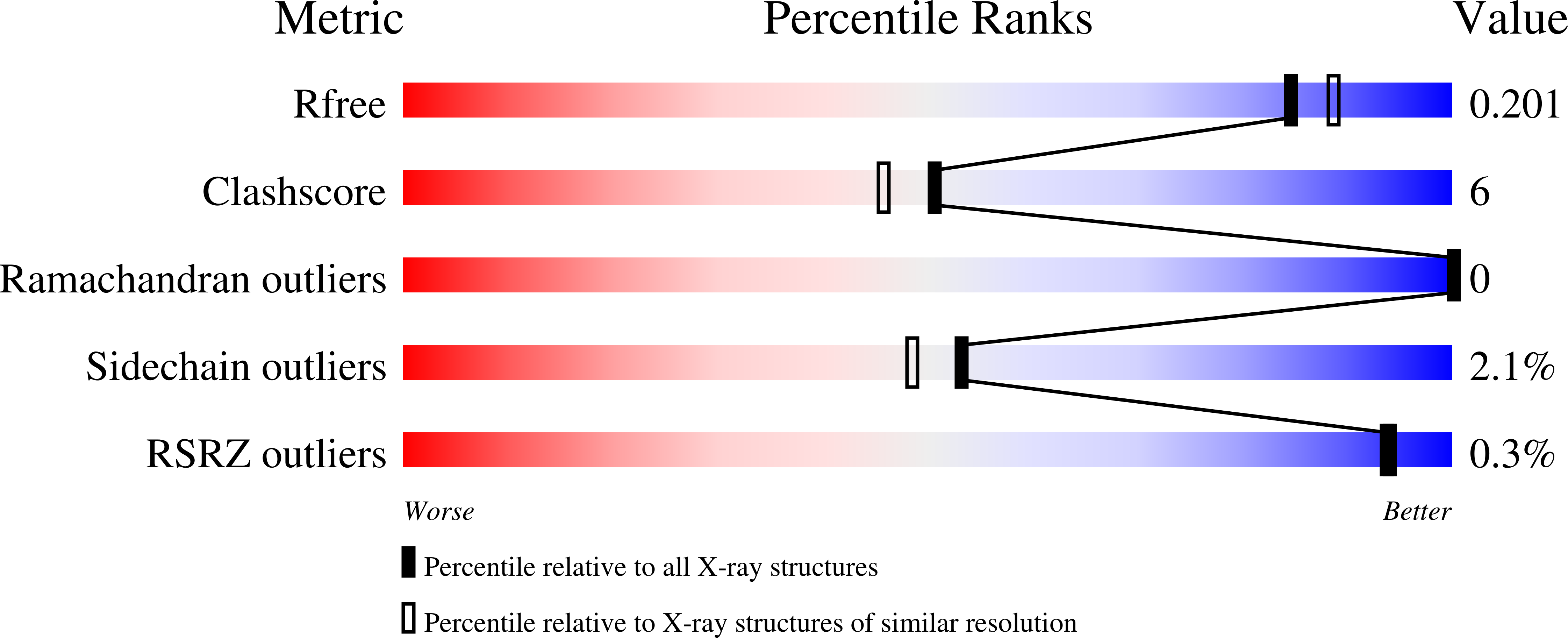
Localization of an Open Reading Frame with Homology to Human Aspartoacylase Upstream from psbA in the Prokaryote Prochlorococcus marinus CCMP 1375 Wolfgang R. Disease relevance of Prochlorococcus The phage psbA genes fall into a clade that includes the psbA genes from their potential Synechococcus and Prochlorococcus hosts and thus this phylogenetic analysis provides evidence to support the idea of the acquisition of these genes by horizontal gene transfer from their cyanobacterial hosts 1. Prochlorococcus possesses a remarkable adaptability to different environmental conditions and might be the most abundant oxyphototrophic organism on earth.
Prochlorococcus a fairly recently discovered cyanobacterium 1988 is the smallest known free-living photosynthetic prokaryote. Prochlorococcus marinus is the type species of an only in 1992 described group of marine cyanobacteria that use divinyl-chlorophyll a and b. In terms of the oceanic food chain these provide the foundation.
Prochlorococcus a fairly recently discovered cyanobacterium 1988 is the smallest known free-living photosynthetic prokaryote. Prochlorococcus a fairly recently discovered cyanobacterium 1988 is the smallest known free-living photosynthetic prokaryote.
For being the smallest known phototrophs the Prochloroccus bacteria play a huge role in the global carbon cycle.
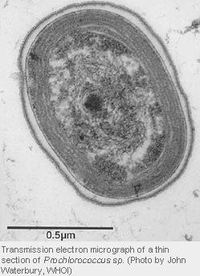
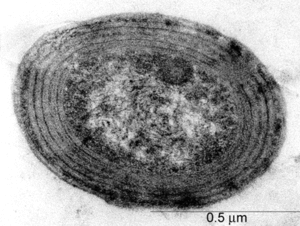
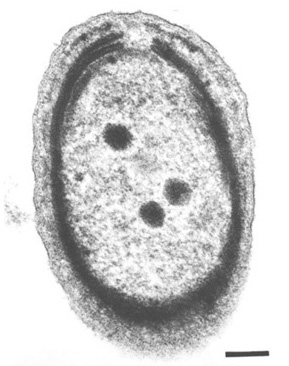
Humans are typically infected through dog and cat bites and infections can lead to swelling and arthritis around joints. It has now been revealed that Prochlorococcus is closely related to the marine cluster A Synechococcus based on analyses using gene sequences from 16S rRNA 16S rDNA and rpoC1 a subunit of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase Palenik and Haselkorn 1992. Despite its small size it. Found in human microbiome Microbes that live anywhere in the human body and are not pathogenic to humans ie. Capable of causing human disease No 0 Yes 1 Plant pathogen. The cytoplasm holds DNA fibrils carboxyzomes and glycogen granules which can be found near or between thylakoids. Hess Humboldt-University Department of Biology Chausseestr. Prochlorococcus a fairly recently discovered cyanobacterium 1988 is the smallest known free-living photosynthetic prokaryote. Prochlorococcus possesses a remarkable adaptability to different environmental conditions and might be the most abundant oxyphototrophic organism on earth.
Urbach et al 1992 1998. It has now been revealed that Prochlorococcus is closely related to the marine cluster A Synechococcus based on analyses using gene sequences from 16S rRNA 16S rDNA and rpoC1 a subunit of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase Palenik and Haselkorn 1992. For being the smallest known phototrophs the Prochloroccus bacteria play a huge role in the global carbon cycle. Prochlorococcus a fairly recently discovered cyanobacterium 1988 is the smallest known free-living photosynthetic prokaryote. Found in human microbiome Microbes that live anywhere in the human body and are not pathogenic to humans ie. Prochlorococcus marinus is the type species of an only in 1992 described group of marine cyanobacteria that use divinyl-chlorophyll a and b. Despite its small size it.

























Post a Comment for "Prochlorococcus Marinus Human Disease"