Subclavian Steal Syndrome Definition
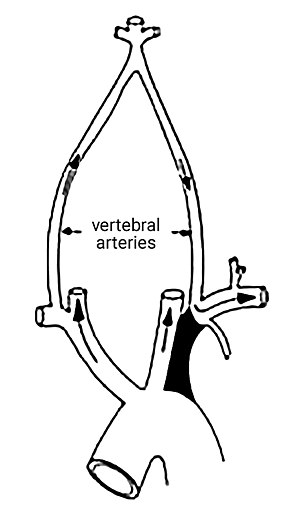
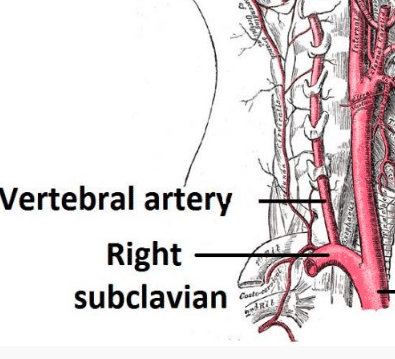
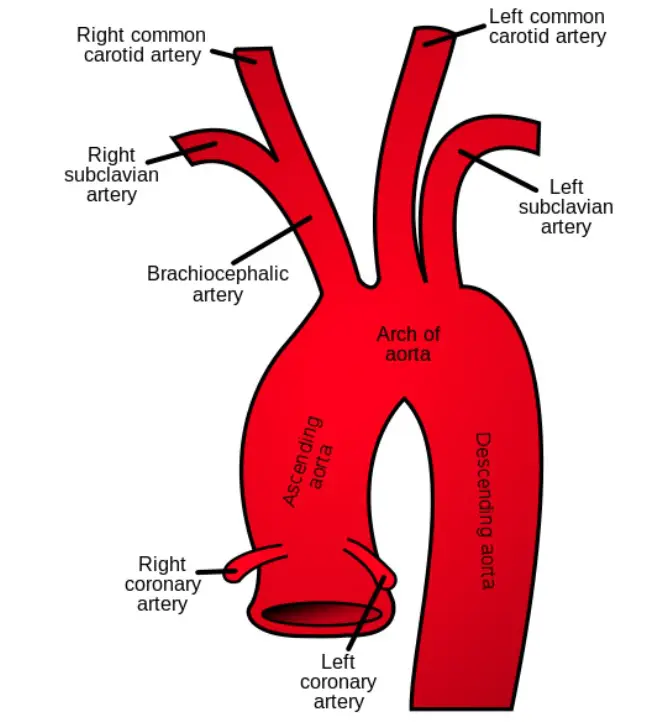
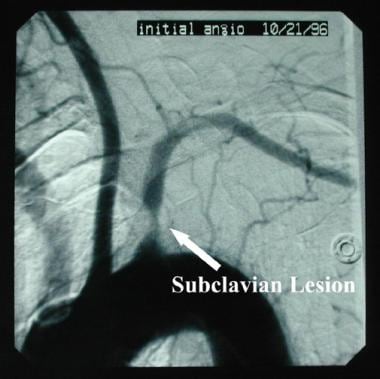
Subclavian steal syndrome definition. Look it up now. Subclavian Steal Syndrome SSS is a condition that results from subclavian artery stenosis proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery. Subclavian steal syndrome implies the presence of significant symptoms due to arterial insufficiency in the brain ie vertebrobasilar insufficiency or upper extremity which is supplied by the subclavian artery figure 1.
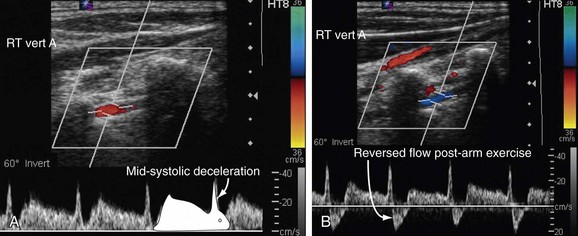
Exercising the arm causes the blood flow to reverse and the subclavian artery steals blood from the vertebral. Subclavian steal refers to a syndrome of symptoms relating to arterial insufficiency in a branch of the subclavian artery stemming from flow reversalattributable to occlusive disease in the subclavian artery proximal to that branch that is usually atheroscleroticin cause. The physiology diagnosis and treatment of.
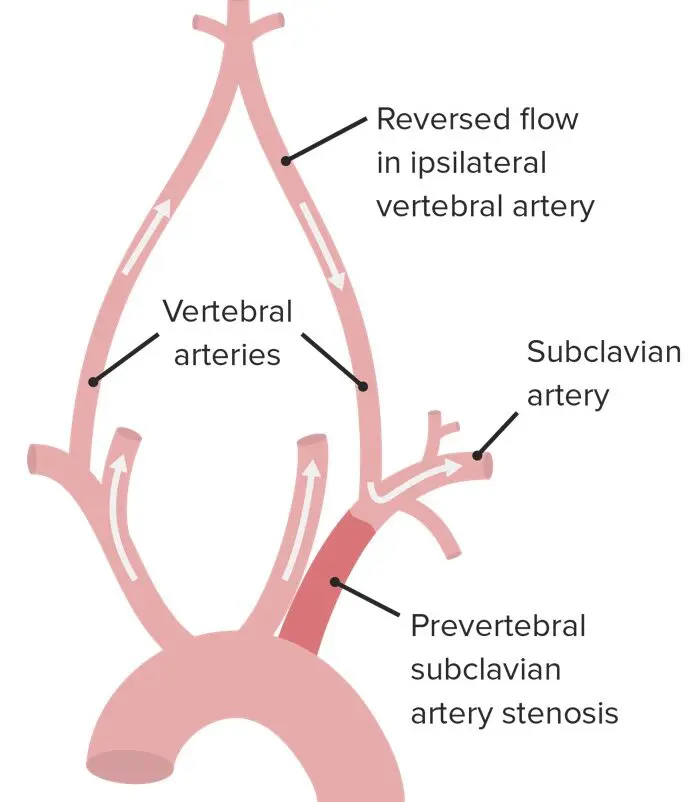
Subclavian Steal Syndrome SSS which is the reverse flow from vertebral artery to subclavian artery was first described in 1977 with an incidence of 044. In medicine subclavian steal syndrome also called subclavian steal phenomenon or subclavian steal steno-occlusive disease is a constellation of signs and symptoms that arise from retrograde flow of blood in the vertebral artery or the internal thoracic artery due to a proximal stenosis andor occlusion of the. A clinically significant reduction in blood supply to the BRAIN STEM and CEREBELLUM ie VERTEBROBASILAR INSUFFICIENCY resulting from reversal of blood flow through the VERTEBRAL ARTERY from occlusion or stenosis of the proximal subclavian or brachiocephalic artery.
A hemodynamic classification into four types of subclavian artery stenosis is also presented. They have been successfully treated by angioplasty of the subclavian artery. Early modifications of the flow in the vertebral artery due to subclavian artery stenosis are presented.
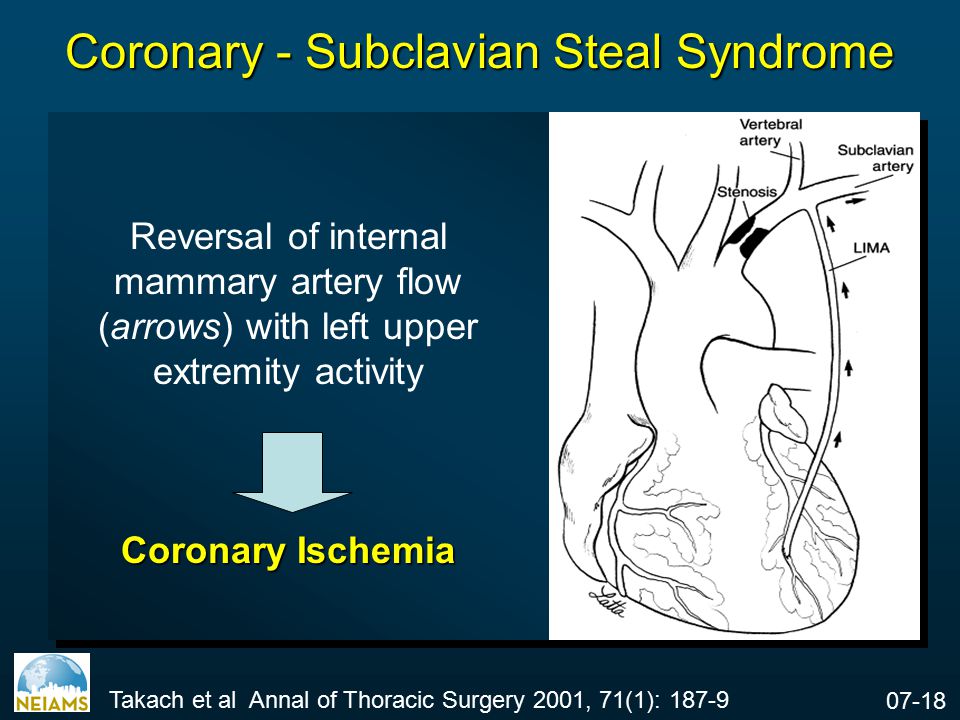
Subclavian steal syndrome is often found in patient with concomitant cardiovascular diseases including lower- extremity peripheral artery disease and coronary artery disease. Some cases of subclavian steal syndrome involve retrograde blood. Carotico subclavian bypass in coronary subclavian steal syndrome.
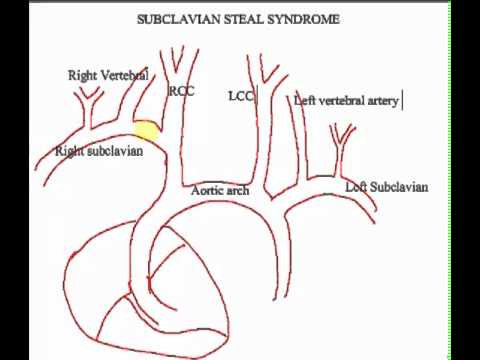
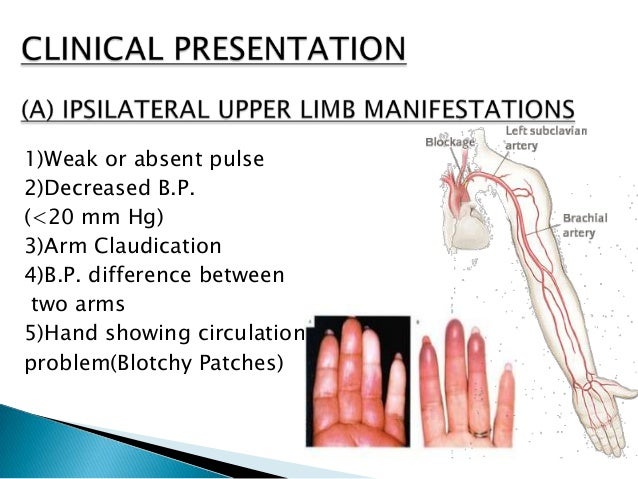
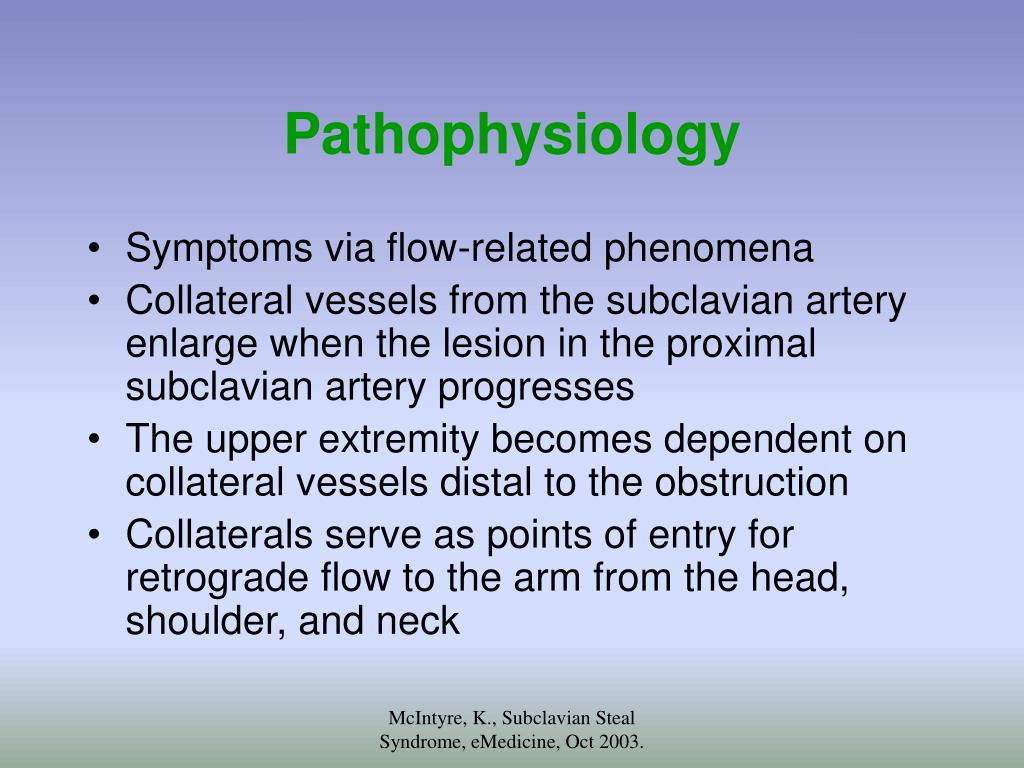
Subclavian steal syndrome is defined as stenosis or occlusion of the subclavian artery proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery with consequent reversal of blood flow in the vertebral artery to supply the distal subclavian artery resulting in neurologic symptoms. The symptoms of cerebral vascular insufficiency not enough blood to the brain when the patient exercises an arm due to obstruction of the subclavian artery before the origin the takeoff of the vertebral artery. In summary subclavian steal syndrome is blood flow reversal in vertebral arteries usually caused by severe stenosis of the subclavian artery or innominate artery.
Subclavian steal syndrome is often found in patient with concomitant cardiovascular diseases including lower- extremity. Subclavian Steal Syndrome SSS refers to a vascular disorder a rare form of periphery artery disease in which a blockage is present in a critical location within one of the Subclavian arteries which gives rise to problems involving the arm and the brain.
Subclavian steal syndrome is defined as stenosis or occlusion of the subclavian artery proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery with consequent reversal of blood flow in the vertebral artery to supply the distal subclavian artery resulting in neurologic symptoms.
In summary subclavian steal syndrome is blood flow reversal in vertebral arteries usually caused by severe stenosis of the subclavian artery or innominate artery. Subclavian Steal Syndrome SSS is a condition that results from subclavian artery stenosis proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery. Subclavian steal syndrome is defined as stenosis or occlusion of the subclavian artery proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery with consequent reversal of blood flow in the vertebral artery to supply the distal subclavian artery resulting in neurologic symptoms. Subclavian steal syndrome is often found in patient with concomitant cardiovascular diseases including lower- extremity. Most patients are asympt. Subclavian Steal Syndrome SSS refers to a vascular disorder a rare form of periphery artery disease in which a blockage is present in a critical location within one of the Subclavian arteries which gives rise to problems involving the arm and the brain. In summary subclavian steal syndrome is blood flow reversal in vertebral arteries usually caused by severe stenosis of the subclavian artery or innominate artery. Subclavian Steal Syndrome SSS which is the reverse flow from vertebral artery to subclavian artery was first described in 1977 with an incidence of 044. The symptoms of cerebral vascular insufficiency not enough blood to the brain when the patient exercises an arm due to obstruction of the subclavian artery before the origin the takeoff of the vertebral artery.
Early modifications of the flow in the vertebral artery due to subclavian artery stenosis are presented. In summary subclavian steal syndrome is blood flow reversal in vertebral arteries usually caused by severe stenosis of the subclavian artery or innominate artery. Exercising the arm causes the blood flow to reverse and the subclavian artery steals blood from the vertebral. A clinically significant reduction in blood supply to the BRAIN STEM and CEREBELLUM ie VERTEBROBASILAR INSUFFICIENCY resulting from reversal of blood flow through the VERTEBRAL ARTERY from occlusion or stenosis of the proximal subclavian or brachiocephalic artery. Subclavian steal syndrome is often found in patient with concomitant cardiovascular diseases including lower- extremity. Subclavian Steal Syndrome SSS is a condition that results from subclavian artery stenosis proximal to the origin of the vertebral artery. Most patients are asympt.































Post a Comment for "Subclavian Steal Syndrome Definition"